
This low hit rate has limited the usage of HTS to research programs capable of screening large compound libraries. However, although traditional HTS often results in multiple hit compounds, some of which are capable of being modified into a lead and later a novel therapeutic, the hit rate for HTS is often extremely low. The method has the advantage of requiring minimal compound design or prior knowledge, and technologies required to screen large libraries have become more efficient. This brute force approach relies on automation to screen high numbers of molecules in search of those that elicit the desired biologic response. Although progress was being made in CADD, the potential for high-throughput screening (HTS) had begun to take precedence as a means for finding novel therapeutics. Some have credited this as being the start of intense interest in the potential for computer-aided drug design (CADD).
On October 5, 1981, Fortune magazine published a cover article entitled the “Next Industrial Revolution: Designing Drugs by Computer at Merck” ( Van Drie, 2007). Finally, computational methods for toxicity prediction and optimization for favorable physiologic properties are discussed with successful examples from literature. In addition, important tools such as target/ligand data bases, homology modeling, ligand fingerprint methods, etc., necessary for successful implementation of various computer-aided drug discovery/design methods in a drug discovery campaign are discussed. We review widely used ligand-based methods such as ligand-based pharmacophores, molecular descriptors, and quantitative structure-activity relationships. Ligand-based methods use only ligand information for predicting activity depending on its similarity/dissimilarity to previously known active ligands. The article discusses theory behind the most important methods and recent successful applications. Structure-based approaches include ligand docking, pharmacophore, and ligand design methods. Structure-based methods are in principle analogous to high-throughput screening in that both target and ligand structure information is imperative. These methods are broadly classified as either structure-based or ligand-based methods. BioScience is ranked among the top journals in its ISI category (Biology) for both Impact Factor and Citation Half-Life.Computer-aided drug discovery/design methods have played a major role in the development of therapeutically important small molecules for over three decades.


Roundtables, forums, and viewpoint articles provide the perspectives of opinion leaders and invite further commentary.
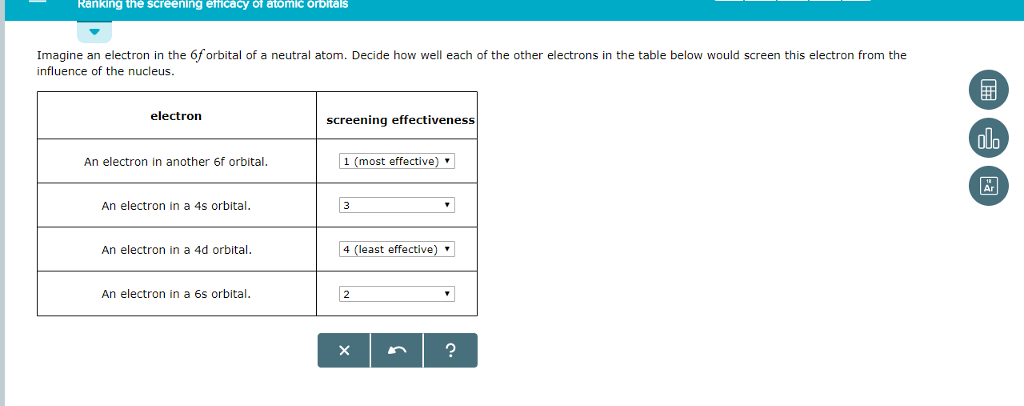
#RANKING THE SCREENING EFFICACY OF ATOMIC ORBITALS PROFESSIONAL#
A peer-reviewed, heavily cited, monthly journal with content written and edited for accessibility to researchers, educators, and students alike, BioScience includes articles about research findings and techniques, advances in biology education, professionally written feature articles about the latest frontiers in biology, discussions of professional issues, book reviews, news about AIBS, a policy column (Washington Watch), and an education column (Eye on Education). Published by the American Institute of Biological Sciences (AIBS), BioScience presents readers with timely and authoritative overviews of current research in biology, accompanied by essays and discussion sections on education, public policy, history, and the conceptual underpinnings of the biological sciences.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
